# grpc-gateway
[](https://travis-ci.org/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway)
grpc-gateway is a plugin of [protoc](http://github.com/google/protobuf).
It reads [gRPC](http://github.com/grpc/grpc-common) service definition,
and generates a reverse-proxy server which translates a RESTful JSON API into gRPC.
This server is generated according to [custom options](https://cloud.google.com/service-management/reference/rpc/google.api#http) in your gRPC definition.
It helps you to provide your APIs in both gRPC and RESTful style at the same time.
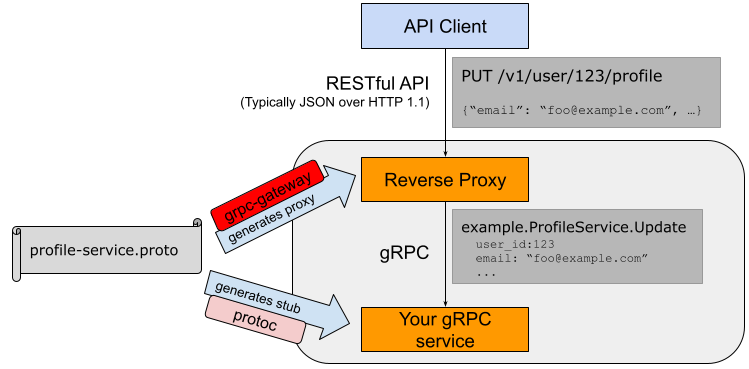
## Background
gRPC is great -- it generates API clients and server stubs in many programming languages, it is fast, easy-to-use, bandwidth-efficient and its design is combat-proven by Google.
However, you might still want to provide a traditional RESTful API as well. Reasons can range from maintaining backwards-compatibility, supporting languages or clients not well supported by gRPC to simply maintaining the aesthetics and tooling involved with a RESTful architecture.
This project aims to provide that HTTP+JSON interface to your gRPC service. A small amount of configuration in your service to attach HTTP semantics is all that's needed to generate a reverse-proxy with this library.
## Installation
First you need to install ProtocolBuffers 3.0.0-beta-3 or later.
```sh
mkdir tmp
cd tmp
git clone https://github.com/google/protobuf
cd protobuf
./autogen.sh
./configure
make
make check
sudo make install
```
Then, `go get -u` as usual the following packages:
```sh
go get -u github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway
go get -u github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/protoc-gen-swagger
go get -u github.com/golang/protobuf/protoc-gen-go
```
## Usage
Make sure that your `$GOPATH/bin` is in your `$PATH`.
1. Define your service in gRPC
your_service.proto:
```protobuf
syntax = "proto3";
package example;
message StringMessage {
string value = 1;
}
service YourService {
rpc Echo(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {}
}
```
2. Add a [custom option](https://cloud.google.com/service-management/reference/rpc/google.api#http) to the .proto file
your_service.proto:
```diff
syntax = "proto3";
package example;
+
+import "google/api/annotations.proto";
+
message StringMessage {
string value = 1;
}
service YourService {
- rpc Echo(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {}
+ rpc Echo(StringMessage) returns (StringMessage) {
+ option (google.api.http) = {
+ post: "/v1/example/echo"
+ body: "*"
+ };
+ }
}
```
3. Generate gRPC stub
```sh
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I. \
-I$GOPATH/src \
-I$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis \
--go_out=plugins=grpc:. \
path/to/your_service.proto
```
It will generate a stub file `path/to/your_service.pb.go`.
4. Implement your service in gRPC as usual
1. (Optional) Generate gRPC stub in the language you want.
e.g.
```sh
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I. \
-I$GOPATH/src \
-I$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis \
--ruby_out=. \
path/to/your/service_proto
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I. \
-I$GOPATH/src \
-I$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis \
--plugin=protoc-gen-grpc=grpc_ruby_plugin \
--grpc-ruby_out=. \
path/to/your/service.proto
```
2. Add the googleapis-common-protos gem (or your language equivalent) as a dependency to your project.
3. Implement your service
5. Generate reverse-proxy
```sh
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I. \
-I$GOPATH/src \
-I$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis \
--grpc-gateway_out=logtostderr=true:. \
path/to/your_service.proto
```
It will generate a reverse proxy `path/to/your_service.pb.gw.go`.
Note: After generating the code for each of the stubs, in order to build the code, you will want to run ```go get .``` from the directory containing the stubs.
6. Write an entrypoint
Now you need to write an entrypoint of the proxy server.
```go
package main
import (
"flag"
"net/http"
"github.com/golang/glog"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/runtime"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
gw "path/to/your_service_package"
)
var (
echoEndpoint = flag.String("echo_endpoint", "localhost:9090", "endpoint of YourService")
)
func run() error {
ctx := context.Background()
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(ctx)
defer cancel()
mux := runtime.NewServeMux()
opts := []grpc.DialOption{grpc.WithInsecure()}
err := gw.RegisterYourServiceHandlerFromEndpoint(ctx, mux, *echoEndpoint, opts)
if err != nil {
return err
}
return http.ListenAndServe(":8080", mux)
}
func main() {
flag.Parse()
defer glog.Flush()
if err := run(); err != nil {
glog.Fatal(err)
}
}
```
7. (Optional) Generate swagger definitions
```sh
protoc -I/usr/local/include -I. \
-I$GOPATH/src \
-I$GOPATH/src/github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/third_party/googleapis \
--swagger_out=logtostderr=true:. \
path/to/your_service.proto
```
## Parameters and flags
`protoc-gen-grpc-gateway` supports custom mapping from Protobuf `import` to Golang import path.
They are compatible to [the parameters with same names in `protoc-gen-go`](https://github.com/golang/protobuf#parameters).
In addition we also support the `request_context` parameter in order to use the `http.Request`'s Context (only for Go 1.7 and above).
This parameter can be useful to pass request scoped context between the gateway and the gRPC service.
`protoc-gen-grpc-gateway` also supports some more command line flags to control logging. You can give these flags together with parameters above. Run `protoc-gen-grpc-gateway --help` for more details about the flags.
## More Examples
More examples are available under `examples` directory.
* `examplepb/echo_service.proto`, `examplepb/a_bit_of_everything.proto`: service definition
* `examplepb/echo_service.pb.go`, `examplepb/a_bit_of_everything.pb.go`: [generated] stub of the service
* `examplepb/echo_service.pb.gw.go`, `examplepb/a_bit_of_everything.pb.gw.go`: [generated] reverse proxy for the service
* `server/main.go`: service implementation
* `main.go`: entrypoint of the generated reverse proxy
To use the same port for custom HTTP handlers (e.g. serving `swagger.json`), gRPC-gateway, and a gRPC server, see [this code example by CoreOS](https://github.com/philips/grpc-gateway-example/blob/master/cmd/serve.go) (and its accompanying [blog post](https://coreos.com/blog/gRPC-protobufs-swagger.html))
## Features
### Supported
* Generating JSON API handlers
* Method parameters in request body
* Method parameters in request path
* Method parameters in query string
* Enum fields in path parameter (including repeated enum fields).
* Mapping streaming APIs to newline-delimited JSON streams
* Mapping HTTP headers with `Grpc-Metadata-` prefix to gRPC metadata (prefixed with `grpcgateway-`)
* Optionally emitting API definition for [Swagger](http://swagger.io).
* Setting [gRPC timeouts](http://www.grpc.io/docs/guides/wire.html) through inbound HTTP `Grpc-Timeout` header.
### Want to support
But not yet.
* bytes fields in path parameter. #5
* Optionally generating the entrypoint. #8
* `import_path` parameter
### No plan to support
But patch is welcome.
* Method parameters in HTTP headers
* Handling trailer metadata
* Encoding request/response body in XML
* True bi-directional streaming. (Probably impossible?)
# Mapping gRPC to HTTP
* [How gRPC error codes map to HTTP status codes in the response](https://github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/blob/master/runtime/errors.go#L15)
* HTTP request source IP is added as `X-Forwarded-For` gRPC request header
* HTTP request host is added as `X-Forwarded-Host` gRPC request header
* HTTP `Authorization` header is added as `authorization` gRPC request header
* Remaining Permanent HTTP header keys (as specified by the IANA [here](http://www.iana.org/assignments/message-headers/message-headers.xhtml) are prefixed with `grpcgateway-` and added with their values to gRPC request header
* HTTP headers that start with 'Grpc-Metadata-' are mapped to gRPC metadata (prefixed with `grpcgateway-`)
* While configurable, the default {un,}marshaling uses [jsonpb](https://godoc.org/github.com/golang/protobuf/jsonpb) with `OrigName: true`.
# Contribution
See [CONTRIBUTING.md](http://github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md).
# License
grpc-gateway is licensed under the BSD 3-Clause License.
See [LICENSE.txt](https://github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/blob/master/LICENSE.txt) for more details.